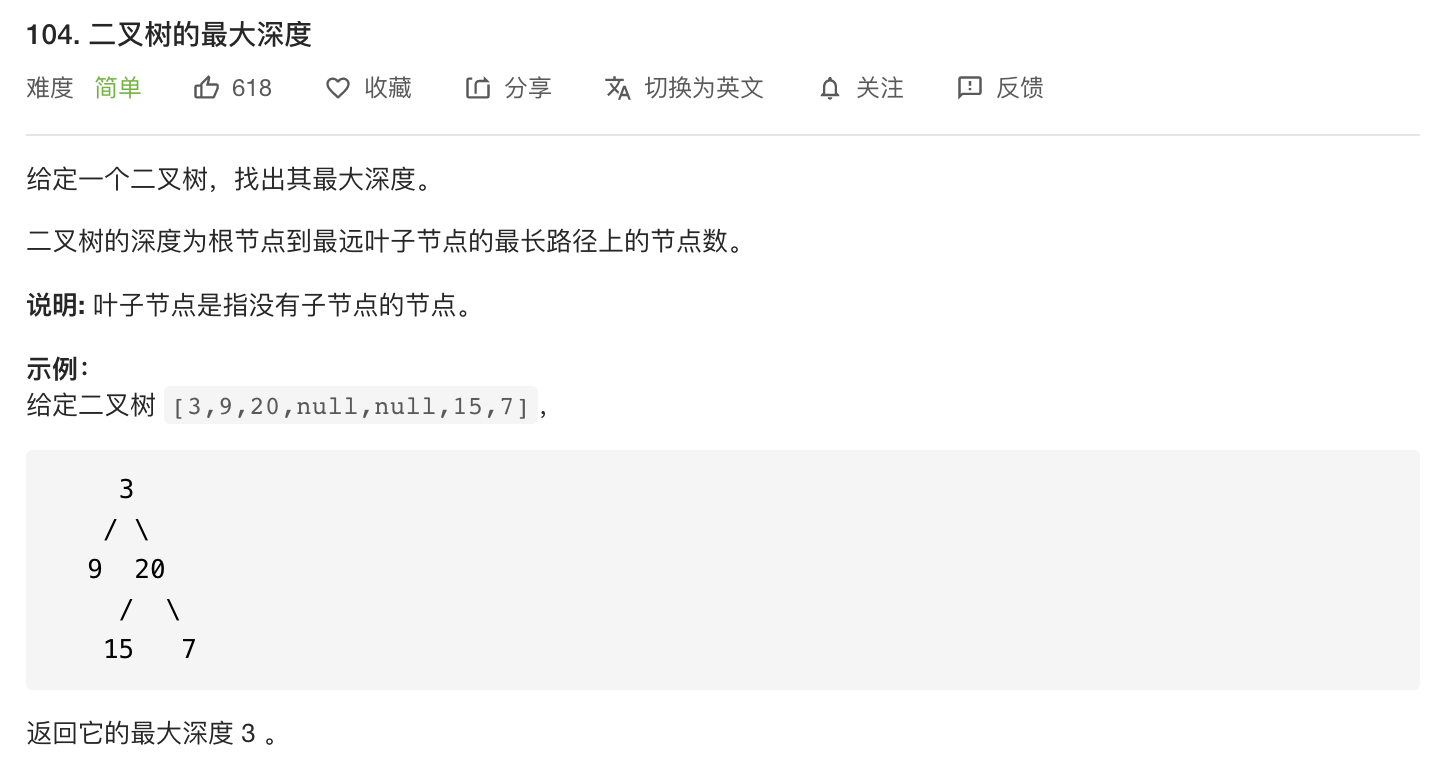
二叉树的最大深度
方法一:DFS递归
一棵二叉树的最大深度可以由左右子树的最大深度+1得到,而左右子树的最大深度又可以由它们自己的子树的最大深度得到,可以按这个思路进行递归。
1 | /** |
2 | * Definition for a binary tree node. |
3 | * public class TreeNode { |
4 | * int val; |
5 | * TreeNode left; |
6 | * TreeNode right; |
7 | * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } |
8 | * } |
9 | */ |
10 | class Solution { |
11 | public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) { |
12 | if(root == null){ |
13 | return 0; |
14 | }else{ |
15 | int leftdepth = maxDepth(root.left); |
16 | int rightdepth = maxDepth(root.right); |
17 | return Math.max(leftdepth, rightdepth)+1; |
18 | } |
19 | } |
20 | } |
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:$O(n)$,其中$n$为二叉树的节点个数,每个节点在递归中被遍历一次。
- 空间复杂度:$O(height)$,$height$表示二叉树的高度。
BFS
可以使用BFS对二叉树进行层序遍历,每遍历一层就将深度+1,因此要记录每一层的节点个数,遍历完一层就要将每一层的节点都出队列。
1 | class Solution { |
2 | public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) { |
3 | if(root == null){ |
4 | return 0; |
5 | } |
6 | Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>(); |
7 | queue.offer(root); |
8 | int ans = 0; |
9 | while(!queue.isEmpty()){ |
10 | int size = queue.size(); |
11 | while(size > 0){ |
12 | TreeNode node = queue.poll(); |
13 | if(node.left != null){ |
14 | queue.offer(node.left); |
15 | } |
16 | if(node.right != null){ |
17 | queue.offer(node.right); |
18 | } |
19 | size--; |
20 | } |
21 | ans++; |
22 | } |
23 | return ans; |
24 | } |
25 | } |
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:$O(n)$。
- 空间复杂度:$O(n)$。