回溯算法总结
最近做了很多需要用到回溯的题,因此做下总结。
回溯法 采用试错的思想,它尝试分步的去解决一个问题。在分步解决问题的过程中,当它通过尝试发现现有的分步答案不能得到有效的正确的解答的时候,它将取消上一步甚至是上几步的计算,再通过其它的可能的分步解答再次尝试寻找问题的答案。回溯法通常用最简单的递归方法来实现,在反复重复上述的步骤后可能出现两种情况:
- 找到一个可能存在的正确的答案;
- 在尝试了所有可能的分步方法后宣告该问题没有答案。
##题型一:排列、组合、子集相关问题
###1.全排列
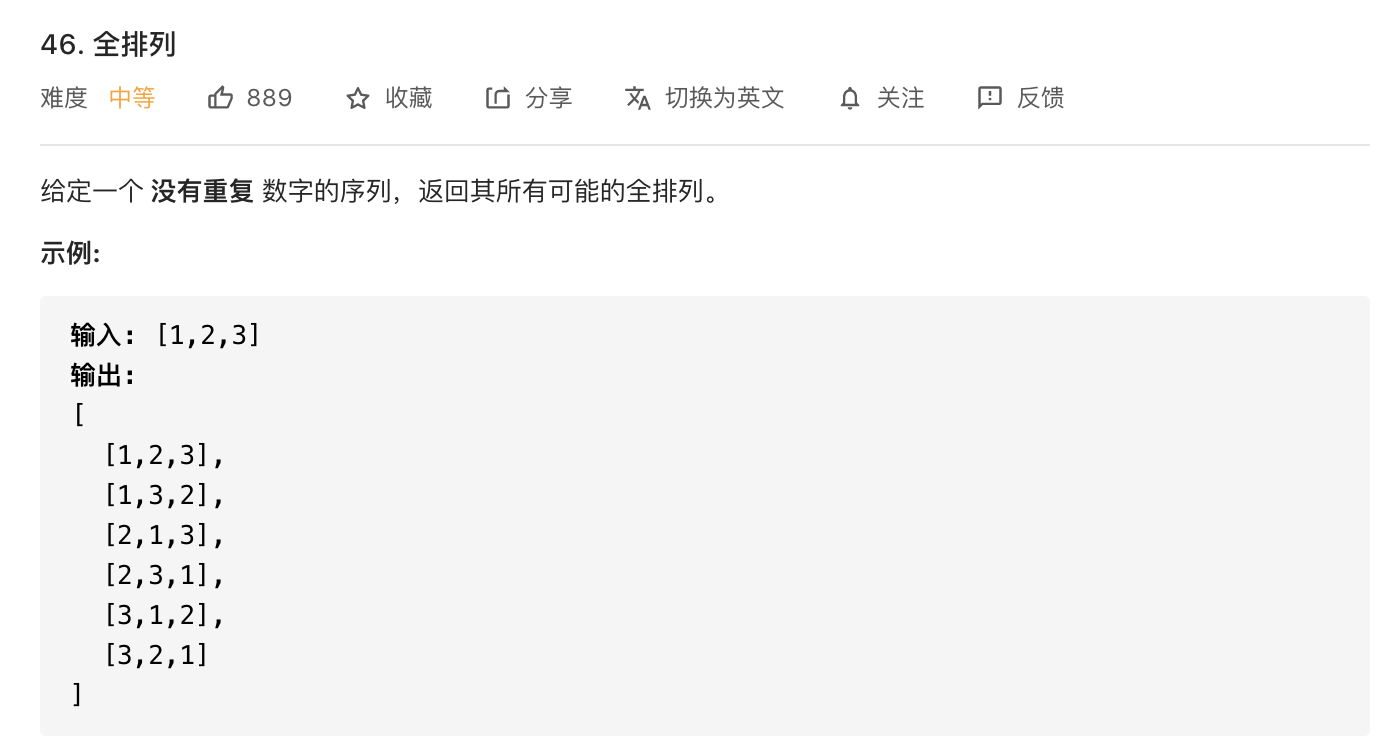
使用visited数组标记访问过的数,被标记的数就不再访问。
1 | class Solution { |
2 | List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); |
3 | List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>(); |
4 | boolean[] visited; |
5 | public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) { |
6 | int n = nums.length; |
7 | visited = new boolean[n]; |
8 | dfs(nums, n); |
9 | return ans; |
10 | } |
11 | |
12 | public void dfs(int[] nums, int n){ |
13 | if(temp.size() == n){ |
14 | ans.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(temp)); |
15 | return; |
16 | } |
17 | for(int i=0; i<n; i++){ |
18 | if(!visited[i]){ |
19 | visited[i] = true; |
20 | temp.add(nums[i]); |
21 | dfs(nums, n); |
22 | visited[i] = false; |
23 | temp.remove(temp.size()-1); |
24 | } |
25 | } |
26 | } |
27 | } |
2.全排列II
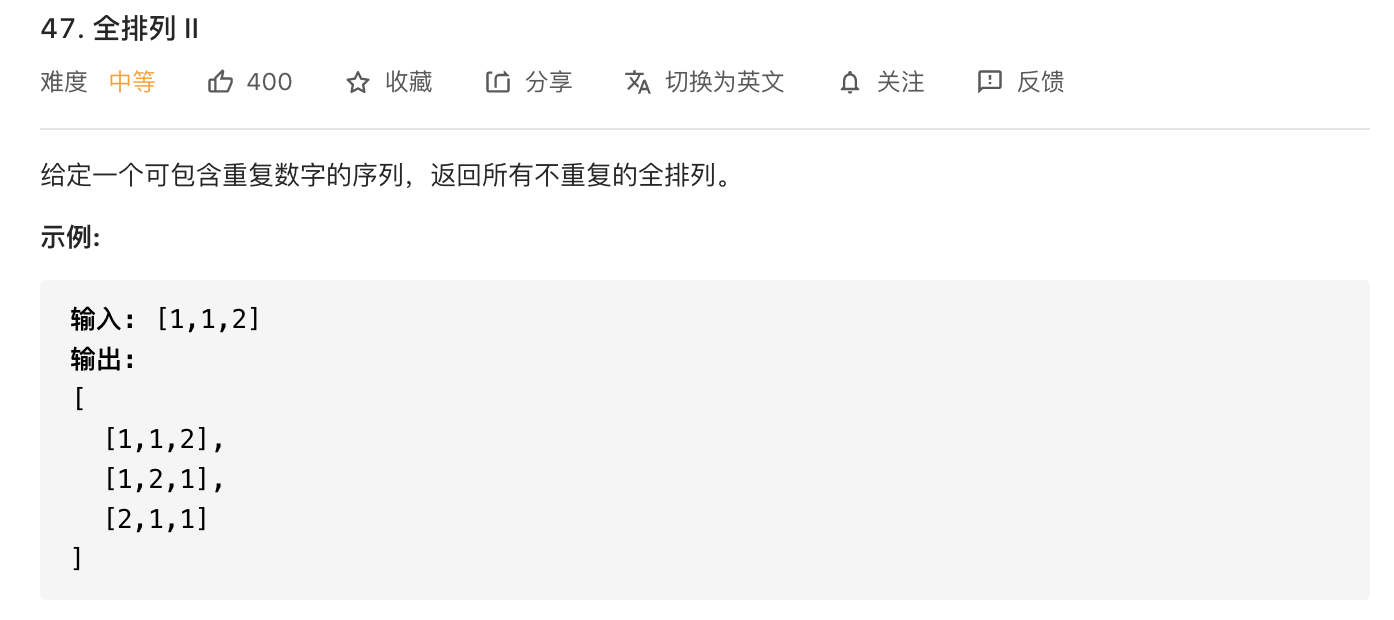
如果按第一题的做法,会出现重复,在枚举到第二个1的时候,会重复枚举第一个1,那么就会有两个[1,1,2]。我们可以先对数组排一个序,然后在枚举第i个数的时候,判断是否与第i-1个数相等,同时判断是否访问过第i-1个数。
1 | class Solution { |
2 | List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); |
3 | List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>(); |
4 | boolean[] visited; |
5 | public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) { |
6 | Arrays.sort(nums); |
7 | int n = nums.length; |
8 | visited = new boolean[n]; |
9 | dfs(nums, n); |
10 | return ans; |
11 | } |
12 | |
13 | public void dfs(int[] nums, int len){ |
14 | if(temp.size() == len){ |
15 | ans.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(temp)); |
16 | return; |
17 | } |
18 | |
19 | for(int i=0; i<len; i++){ |
20 | if(visited[i]){ |
21 | continue; |
22 | } |
23 | // 关键,剪去重复情况 |
24 | if(i>0 && nums[i]==nums[i-1] && !visited[i-1]){ |
25 | continue; |
26 | } |
27 | visited[i] = true; |
28 | temp.add(nums[i]); |
29 | dfs(nums, len); |
30 | visited[i] = false; |
31 | temp.remove(temp.size()-1); |
32 | } |
33 | } |
34 | } |
其中
1 | if(i>0 && nums[i]==nums[i-1] && !visited[i-1]){continue;} |
也可以写成
1 | if(i>0 && nums[i]==nums[i-1] && visited[i-1]){continue;} |
仅仅是剪枝顺序的不同。
3.组合总和

这里需要设置一个起始下标cur,因为可以无限制重复被选取,同时不能包含重复的组合,所以每次递归进行枚举的时候从cur开始枚举。
1 | class Solution { |
2 | List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); |
3 | List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>(); |
4 | public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) { |
5 | dfs(candidates, target, 0, 0); |
6 | return ans; |
7 | } |
8 | |
9 | public void dfs(int[] candidates, int target, int cur, int sum){ |
10 | if(target == sum){ |
11 | ans.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(temp)); |
12 | return; |
13 | }else if(target < sum){ |
14 | return; |
15 | } |
16 | if(cur == candidates.length){ |
17 | return; |
18 | } |
19 | for(int i=cur; i<candidates.length; i++){ |
20 | sum += candidates[i]; |
21 | temp.add(candidates[i]); |
22 | // 起始下标不变,因为可以重复选取 |
23 | dfs(candidates, target, i, sum); |
24 | // 回溯 |
25 | sum -= candidates[i]; |
26 | temp.remove(temp.size()-1); |
27 | } |
28 | // 第二种写法,两种情况,选择当前下标数和选择跳过当前数 |
29 | // sum += candidates[cur]; |
30 | // temp.add(candidates[cur]); |
31 | // dfs(candidates, target, cur, sum); |
32 | // sum -= candidates[cur]; |
33 | // temp.remove(temp.size()-1); |
34 | // dfs(candidates, target, cur+1, sum); |
35 | } |
36 | } |
4.组合总和II
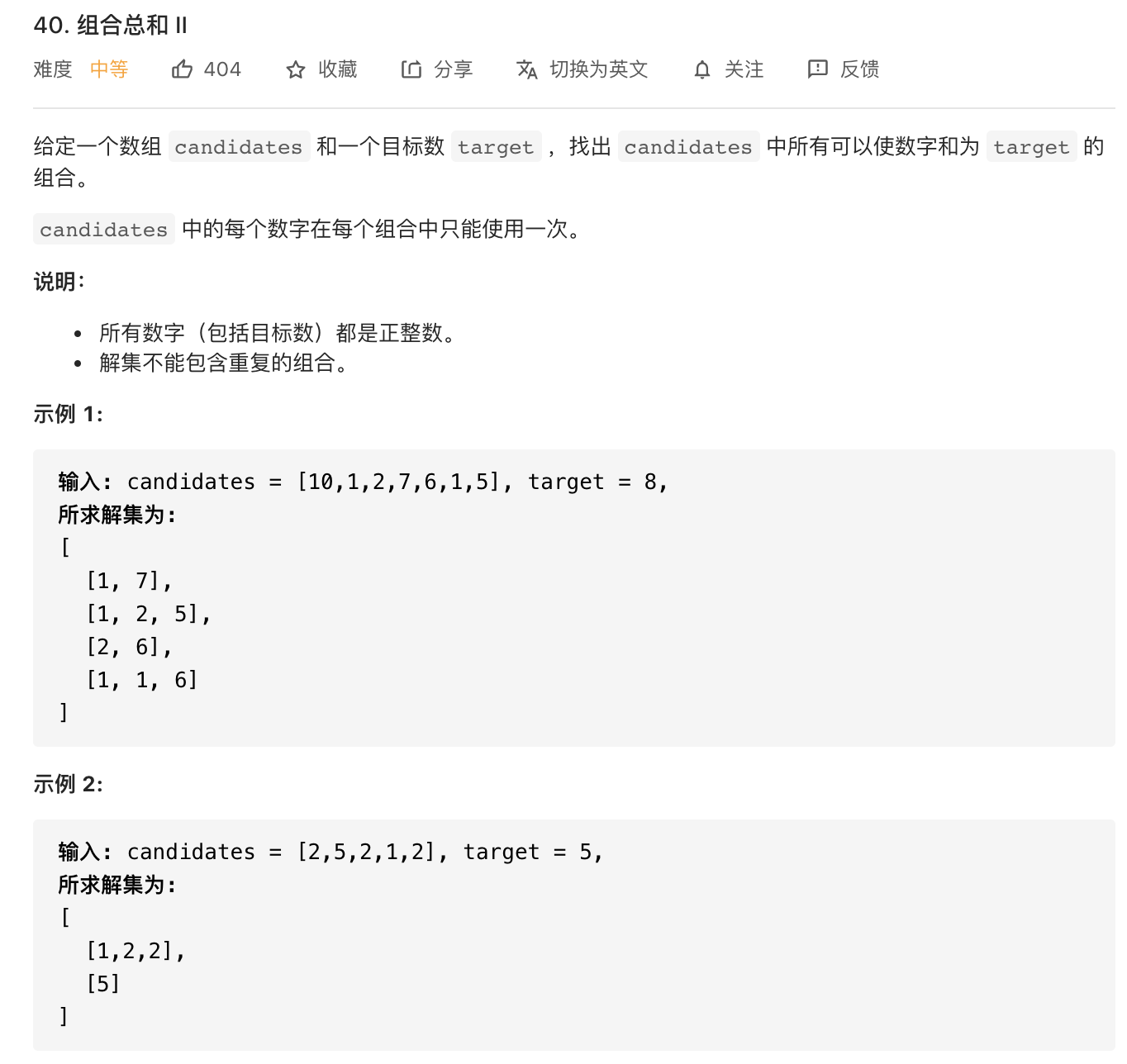
这里也需要一个起始下标cur,但不同的是数组中存在重复的数且每个数只能使用一次,因此我们首先需要对数组排个序,在循环中判断第i个数是否与第i-1个数相等,相等就跳过,不同的话就进行下一次递归,递归的起始下标因为只能使用一次数,所以起始下标需要+1。
1 | class Solution { |
2 | List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); |
3 | List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>(); |
4 | public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) { |
5 | Arrays.sort(candidates); |
6 | dfs(candidates, target, 0, 0); |
7 | return ans; |
8 | } |
9 | |
10 | public void dfs(int[] candidates, int target, int cur, int sum){ |
11 | if(target == sum){ |
12 | ans.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(temp)); |
13 | return; |
14 | } |
15 | if(sum>target || cur>=candidates.length){ |
16 | return; |
17 | } |
18 | for(int i=cur; i<candidates.length; i++){ |
19 | // 避免重复 |
20 | if(i > cur && candidates[i]==candidates[i-1]){ |
21 | continue; |
22 | } |
23 | sum += candidates[i]; |
24 | temp.add(candidates[i]); |
25 | // 起始下标+1,因为只能选取一次 |
26 | dfs(candidates, target, i+1, sum); |
27 | sum -= candidates[i]; |
28 | temp.remove(temp.size()-1); |
29 | } |
30 | } |
31 | } |
5.组合
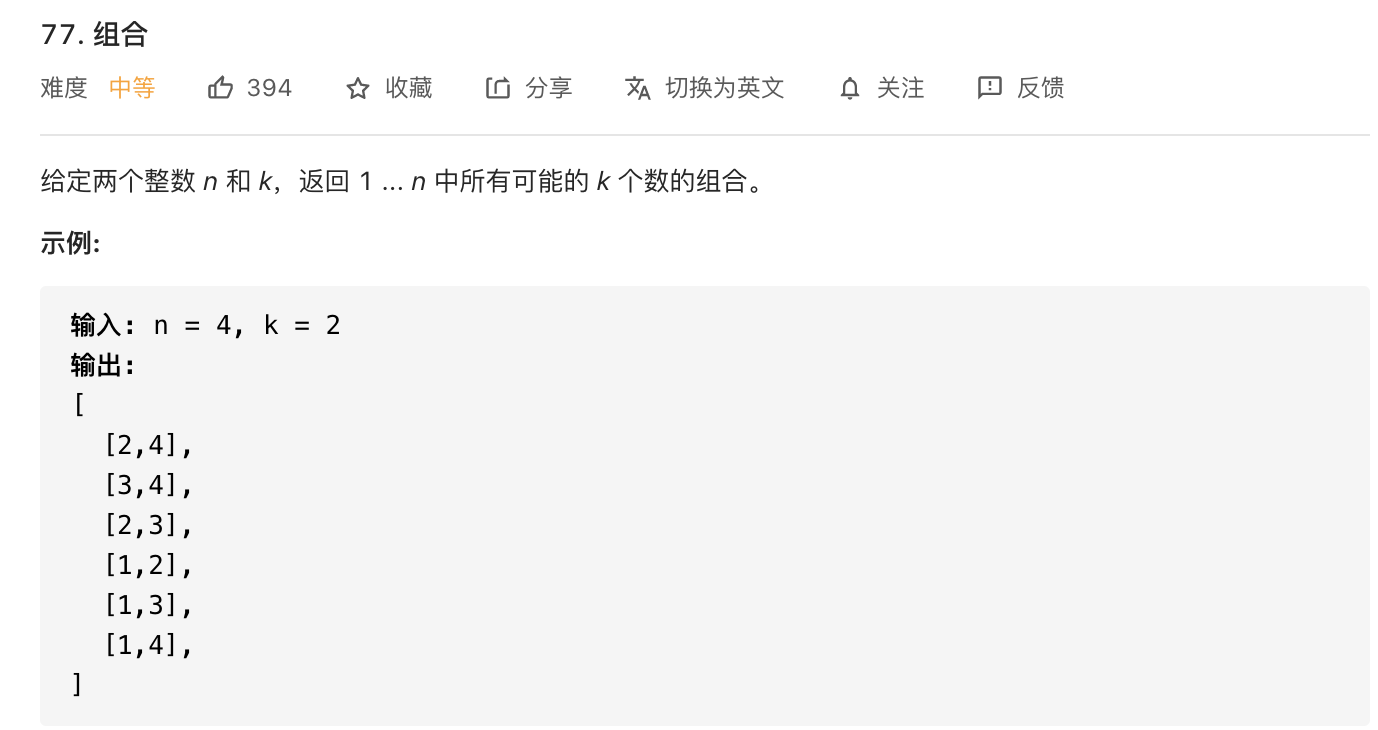
这里的隐含条件就是每个数只能选一次,因此每次递归时起始下标cur要+1。
1 | class Solution { |
2 | List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); |
3 | List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>(); |
4 | public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) { |
5 | dfs(1, n, k); |
6 | return ans; |
7 | } |
8 | |
9 | public void dfs(int cur, int n, int k){ |
10 | // 剪枝,如果当前list大小+剩余的数的个数还小于k |
11 | // 就不可能是一个满足条件的组合 |
12 | if(temp.size()+(n-cur)+1 < k){ |
13 | return; |
14 | } |
15 | if(temp.size() == k){ |
16 | ans.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(temp)); |
17 | return; |
18 | } |
19 | for(int i=cur; i<=n; i++){ |
20 | temp.add(i); |
21 | dfs(i+1, n, k); |
22 | temp.remove(temp.size()-1); |
23 | } |
24 | } |
25 | } |
6.子集
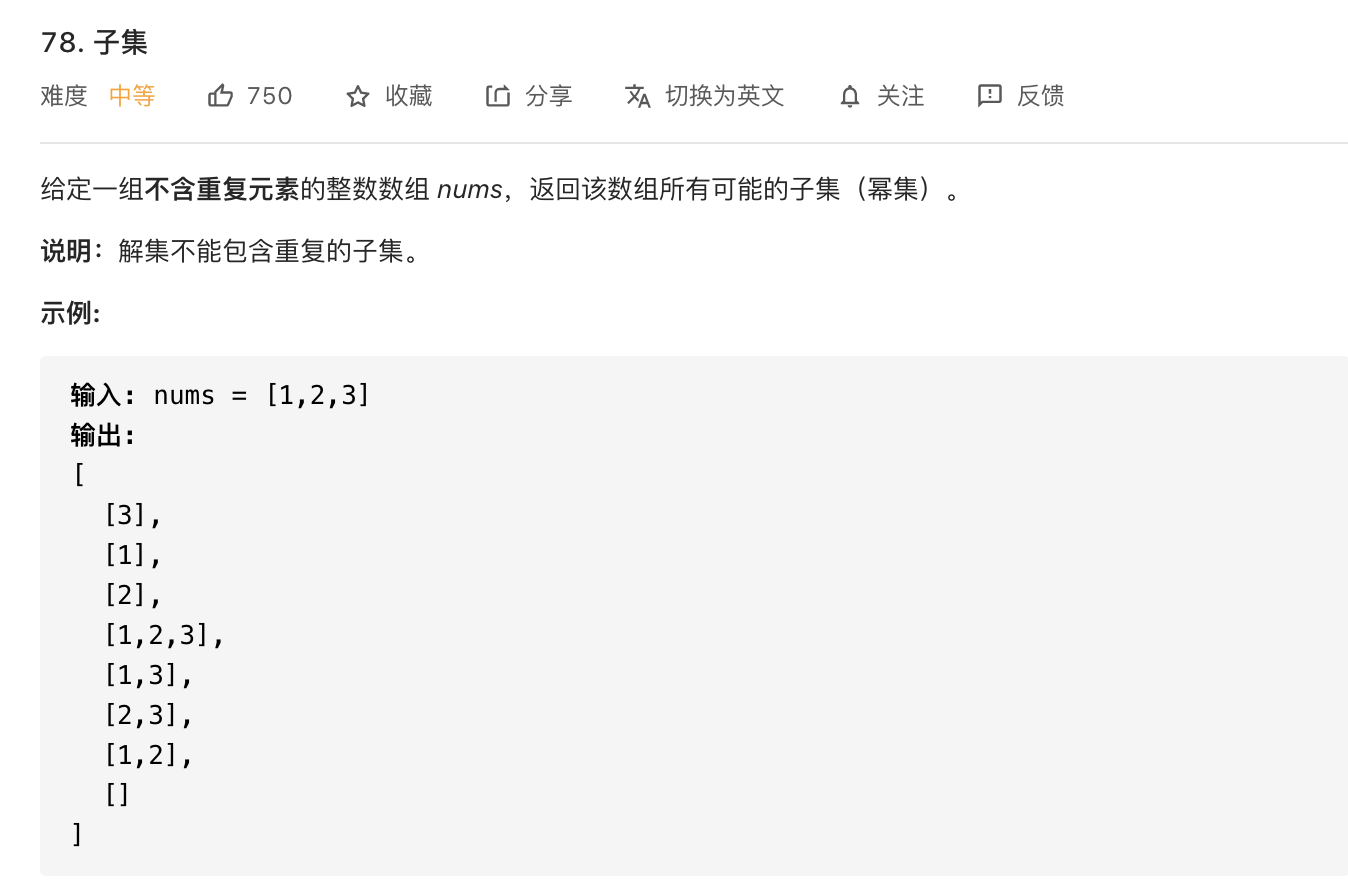
注意每个数只能选一次。
1 | class Solution { |
2 | List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); |
3 | List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>(); |
4 | public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) { |
5 | int n = nums.length; |
6 | dfs(nums, 0, n); |
7 | return ans; |
8 | } |
9 | public void dfs(int[] nums, int cur, int len){ |
10 | ans.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(temp)); |
11 | for(int i=cur; i<len; i++){ |
12 | temp.add(nums[i]); |
13 | dfs(nums, i+1, len); |
14 | temp.remove(temp.size()-1); |
15 | } |
16 | } |
17 | } |
7.子集II
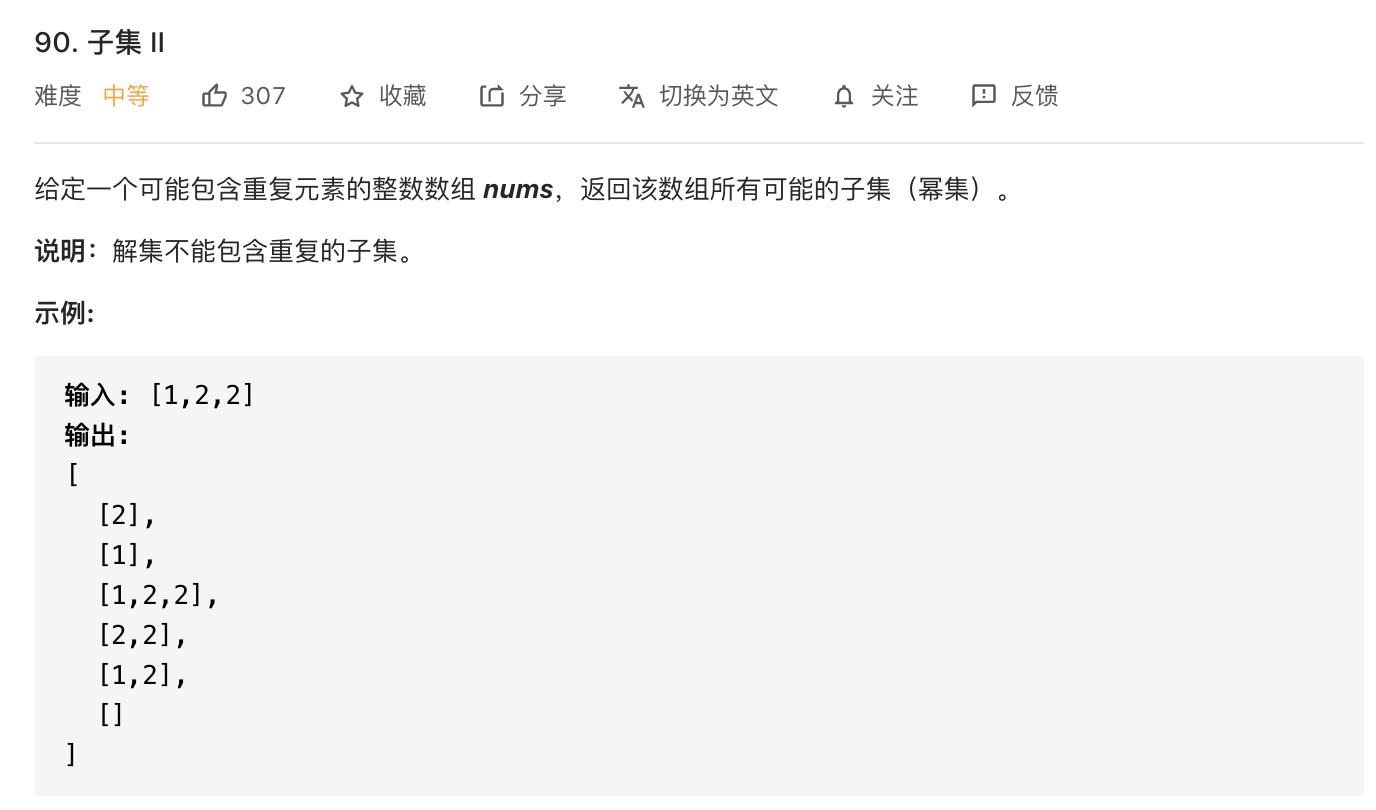
这里需要注意有重复的数,所以剪枝技巧还是和前面一样,先对数组进行排序,再判断第i个数是否与第i-1个数相等。由于这里是求子集,每个数可取可不取,所以不必设置访问标记数组,而在全排列中,因为每个数都必须要用到,所以还需要额外设置访问标记数组visited。
1 | class Solution { |
2 | List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); |
3 | List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>(); |
4 | public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) { |
5 | Arrays.sort(nums); |
6 | int n = nums.length; |
7 | dfs(nums, n, 0); |
8 | return ans; |
9 | } |
10 | public void dfs(int[] nums, int len, int cur){ |
11 | ans.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(temp)); |
12 | for(int i=cur; i<len; i++){ |
13 | if(i>cur && nums[i]==nums[i-1]){ |
14 | continue; |
15 | } |
16 | temp.add(nums[i]); |
17 | dfs(nums, len, i+1); |
18 | temp.remove(temp.size()-1); |
19 | } |
20 | } |
21 | } |
8.第k个排列

这里可以利用剪枝技巧直接找到第k个排列。例如n=3时,对于1开头的排列组合有两种,123和132,对于2开头的排列组合也是两种,213和231,以此类推。对于12开头的排列组合有一种。那么我们就可以利用这一性质进行剪枝。
1 | class Solution { |
2 | boolean[] used; |
3 | int[] factorial; |
4 | int n; |
5 | int k; |
6 | public String getPermutation(int n, int k) { |
7 | this.n = n; |
8 | this.k = k; |
9 | calculateFactorial(n); |
10 | used = new boolean[n+1]; |
11 | |
12 | StringBuilder path = new StringBuilder(); |
13 | dfs(0, path); |
14 | return path.toString(); |
15 | } |
16 | |
17 | public void dfs(int index, StringBuilder path){ |
18 | // 找到该排列 |
19 | if(index == n){ |
20 | return; |
21 | } |
22 | // 计算出[index...n-1]有多少种排列个数 |
23 | int cnt = factorial[n-1-index]; |
24 | for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){ |
25 | // 每个数只能使用一次 |
26 | if(used[i]){ |
27 | continue; |
28 | } |
29 | // 第k个排列在下一个分支 |
30 | if(k > cnt){ |
31 | k -= cnt; |
32 | continue; |
33 | } |
34 | path.append(i); |
35 | used[i] = true; |
36 | dfs(index+1, path); |
37 | return; |
38 | } |
39 | } |
40 | // 预处理,计算出阶乘 |
41 | public void calculateFactorial(int n){ |
42 | factorial = new int[n+1]; |
43 | factorial[0] = 1; |
44 | for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){ |
45 | factorial[i] = factorial[i-1] * i; |
46 | } |
47 | } |
48 | } |
9.复原IP地址
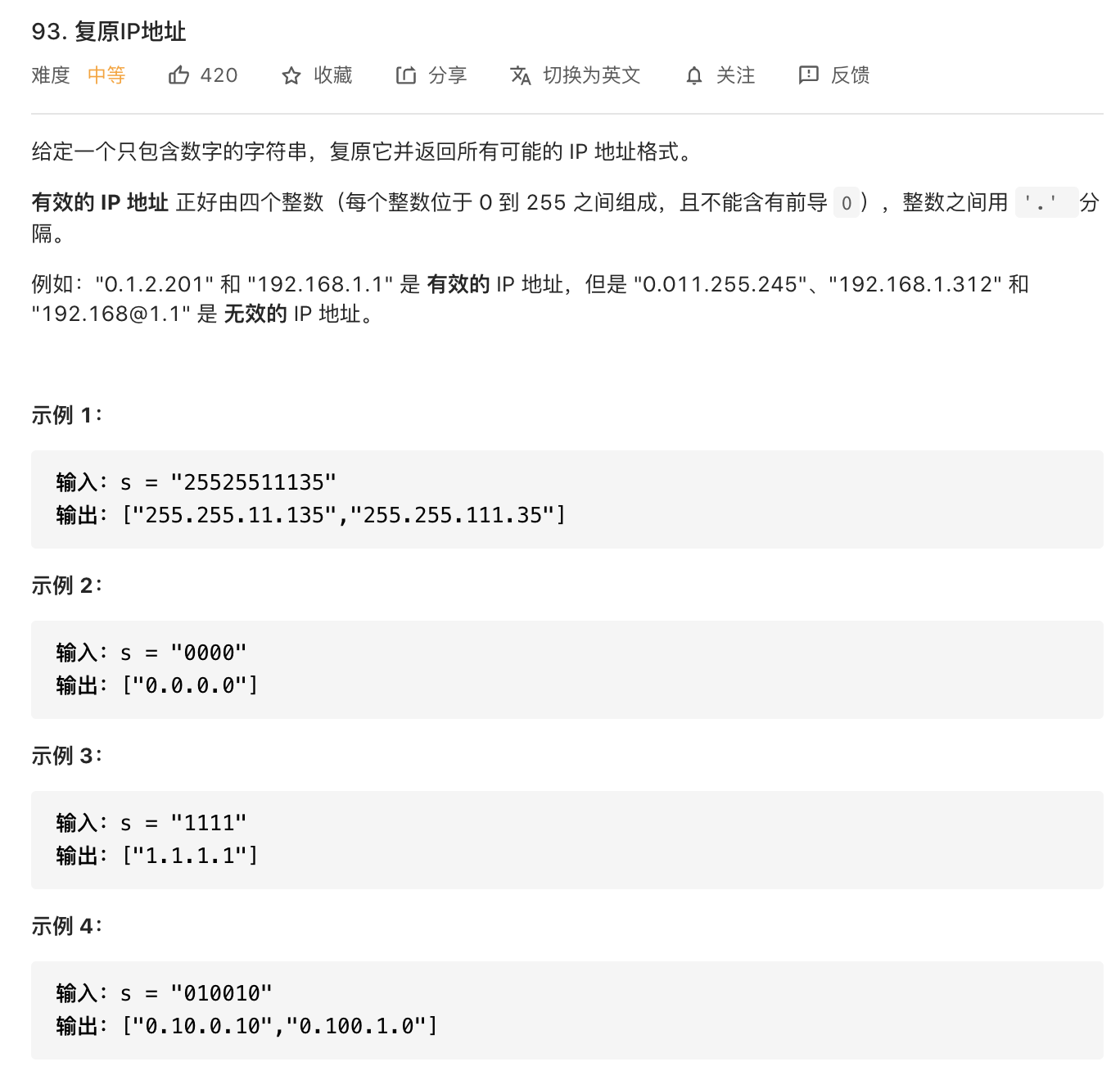
需要一个计数器来记录已有多少段IP地址,如果已经满4段IP就判断是否能够组成IP地址,另外需要一个起始下标cur记录当前位置。
1 | class Solution { |
2 | static final int SEG_COUNT = 4; |
3 | List<String> ans = new ArrayList<String>(); |
4 | int[] segments = new int[SEG_COUNT]; |
5 | |
6 | public List<String> restoreIpAddresses(String s) { |
7 | segments = new int[SEG_COUNT]; |
8 | dfs(s, 0, 0); |
9 | return ans; |
10 | } |
11 | |
12 | public void dfs(String s, int segId, int segStart) { |
13 | // 如果找到了 4 段 IP 地址并且遍历完了字符串,那么就是一种答案 |
14 | if (segId == SEG_COUNT) { |
15 | if (segStart == s.length()) { |
16 | StringBuffer ipAddr = new StringBuffer(); |
17 | for (int i = 0; i < SEG_COUNT; ++i) { |
18 | ipAddr.append(segments[i]); |
19 | if (i != SEG_COUNT - 1) { |
20 | ipAddr.append('.'); |
21 | } |
22 | } |
23 | ans.add(ipAddr.toString()); |
24 | } |
25 | return; |
26 | } |
27 | |
28 | // 如果还没有找到 4 段 IP 地址就已经遍历完了字符串,那么提前回溯 |
29 | if (segStart == s.length()) { |
30 | return; |
31 | } |
32 | |
33 | // 由于不能有前导零,如果当前数字为 0,那么这一段 IP 地址只能为 0 |
34 | if (s.charAt(segStart) == '0') { |
35 | segments[segId] = 0; |
36 | dfs(s, segId + 1, segStart + 1); |
37 | } |
38 | |
39 | // 一般情况,枚举每一种可能性并递归 |
40 | int addr = 0; |
41 | for (int segEnd = segStart; segEnd < s.length(); ++segEnd) { |
42 | addr = addr * 10 + (s.charAt(segEnd) - '0'); |
43 | if (addr > 0 && addr <= 255) { |
44 | segments[segId] = addr; |
45 | dfs(s, segId + 1, segEnd + 1); |
46 | } else { |
47 | break; |
48 | } |
49 | } |
50 | } |
51 | } |
10.小结
可以看到这些题目的大概框架是一样的,在开始搜索时,先判断是否满足答案条件,满足就返回,否则就进行下一步搜索,下一步的搜索可以利用一个循环来进行,循环开始可以是当前下标cur,也可以是从头开始,具体需要看题目。在循环里可以根据题目条件进行一些剪枝,例如不包含重复答案等等,在搜索返回后记得要回溯,将改变的状态恢复到之前的状态。